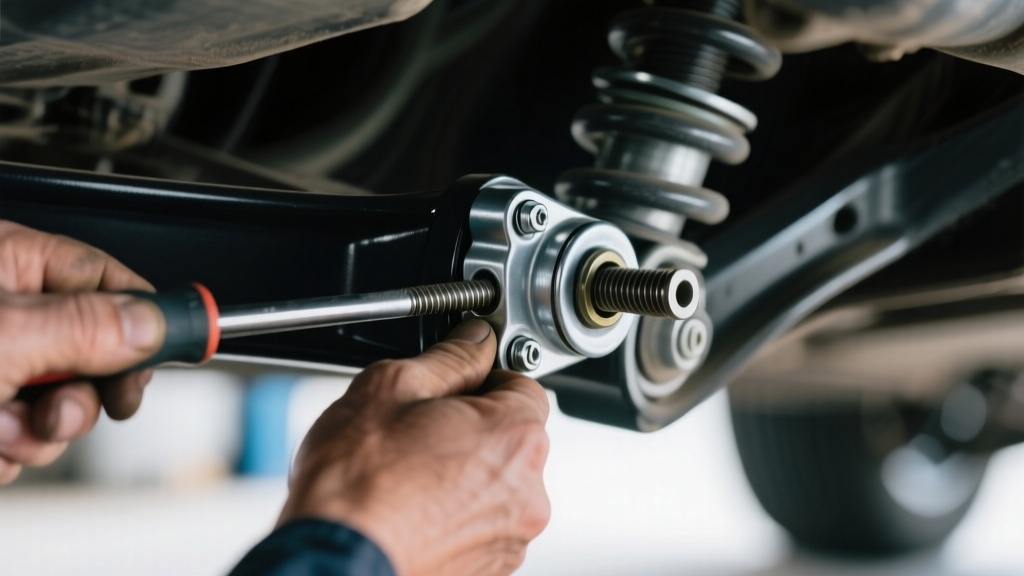
To hook up stabilizer bars, first securely mount the brackets to your vehicle’s frame, ensuring proper alignment and clearance. Lubricate the D-bushings before sliding them onto the bar, then loosely attach U-plates and fasten with bolts to the brackets.
Connect the end links vertically to control arms, drilling holes if necessary, and tighten all hardware to manufacturer torque specs using a torque wrench. Verify alignment to prevent binding or looseness. Following these steps optimizes stability and handling. Further steps ensure precise tuning and safety.
Key Takeaways
- Park the vehicle on a level surface, lift securely with jack stands, and remove wheels before starting stabilizer bar installation.
- Position and drill mounting brackets near welds, then secure brackets with properly torqued bolts ensuring flush alignment.
- Lubricate D-bushings, install the stabilizer bar with U-plates, and loosely bolt to frame brackets using correct hardware.
- Attach end links vertically on control arms with vehicle weight applied, drilling necessary holes for bracket mounting.
- Center the stabilizer bar using a level, adjust link rotation to prevent binding, and torque all fasteners to specified values.
Purpose and Benefits of Stabilizer Bars
Why do stabilizer bars play a crucial role in vehicle dynamics? They reduce body roll by connecting the left and right wheels with a torsion spring mechanism, keeping your vehicle level during cornering. This improves stability and control by maintaining consistent control arm angles, ensuring better tire contact with the road.
Stabilizer bars increase suspension roll stiffness, lowering the vehicle’s center of gravity and enhancing handling precision. They are typically made of U-shaped metal designed to fit the vehicle chassis precisely, similar to how reinforced sidewalls enhance trailer tire durability and performance.
By resisting twisting forces, they transfer load from the compressed side to the extended side, limiting body lean and improving grip during turns. Additionally, you can tune handling balance by adjusting front and rear roll stiffness, customizing understeer or oversteer characteristics.
Tools Needed for Installation
When you’re getting ready to install a stabilizer bar, it’s important to gather the right tools. You’ll want to have a good range of socket wrenches, usually between 16mm and 27mm. These will help you tackle the various bolts you’ll encounter during the installation process.
Choosing the correct tools can also help maintain optimal performance of your vehicle’s suspension system. Now, don’t forget to grab some combination or adjustable wrenches as well. They’ll come in handy, especially for those tight spaces where it’s tough to maneuver.
And here’s a little tip: make sure you have the right drill bits on hand too. You’ll need sizes like 1/4”, 1/2”, 5/8”, and maybe even 17/32” for preparing those mounting holes accurately. Additionally, having labeled components ready ensures each part is installed in the correct location, making the process more efficient and accurate.
Essential Drill Bit Sizes
When installing stabilizer bars, selecting the correct drill bit sizes is crucial to guarantee secure mounting and proper fitment.
Use 7/16″ and 1/2″ drill bits to enlarge frame holes for rivnuts or bolts, especially on thicker frame sections.
For thinner materials near 1/8” thickness, opt for 9/32″ or 11/32″ bits, typical in friction sway control kit setups.
A 13/64″ drill bit suits some bolt hole drilling tasks, while 15/16″ is reserved for specific rear stabilizer bar frame holes.
Always drill pilot holes with smaller bits first to prevent cracking or misalignment.
Ensure your drill bits are sharp and appropriate for metal cutting to avoid heat buildup and deformation.
Mark drill points precisely, drill slowly, and avoid damaging brake or fuel lines during installation.
Using high-quality tools and materials helps maintain durability and safety during the installation process.
Required Wrench and Socket
Although stabilizer bar installation involves various fasteners, having the correct wrenches and sockets is critical to guarantee secure and efficient assembly.
You’ll need a combination of open-ended, ratcheting, and pass-through wrenches, along with sockets matching common sizes like 17mm for sway bar link fasteners and 21mm for shock retaining nuts.
Using a torque wrench is essential to apply the recommended 23–33 foot-pounds without over-tightening. Additionally, using an adapter for an 18mm wrench can prevent stripping of fasteners during installation. Proper maintenance and durable materials contribute to the longevity of the stabilizer bar system.
| Tool Type | Common Sizes/Use |
|---|---|
| Sockets | 14mm, 16mm, 17mm, 21mm, 24mm |
| Wrenches | Open-ended, ratcheting, pass-through |
| Specialized Tools | Pass-through socket sets, breaker bars |
Equip yourself with these tools for a precise, secure stabilizer bar hook-up.
Preparing for Installation
Before starting the installation, verify the vehicle is securely parked on a level surface with the parking brake engaged and wheels chocked to prevent movement.
Ensure the vehicle is parked level, parking brake set, and wheels chocked before beginning installation.
On front-wheel-drive models, turn the steering wheel away from the work side to improve access.
Next, position the jack under the manufacturer’s recommended lifting points and raise the vehicle.
Securely place jack stands at both frame rails and rear axle, ensuring they’re rated for the vehicle’s weight and stable. Proper safety measures are crucial to avoid accidents during the process.
Remove the front wheels after confirming the vehicle is supported properly. Assemble all necessary tools, including socket and open-end wrenches sized for your model, a torque wrench, and penetrating fluid.
Conduct a thorough inspection of the existing sway bar routing, mounting brackets, and clearances, documenting reference points to align the new installation accurately. Checking for waste breakdown efficiency in nearby systems can provide insight into maintaining optimal vehicle performance.
Installing the Mounting Bracket
Since accurate bracket placement is essential for stability, position the mounting bracket tight to the weld and about one inch up from the bottom of the gusset before drilling any holes. Proper alignment helps ensure maximum durability under stress.
Hold the bracket firmly against the weld, mark hole locations using the bracket as a template, then use a 5/8-inch drill bit to create center point indentations. Predrill with a 1/4-inch bit, then drill final holes with a 1/2-inch bit, ensuring straight alignment for bolt fitment.
Secure the bracket with supplied bolts, tighten to the specified torque, and leave at least three threads exposed. Confirm bracket alignment and flush mounting before finalizing. This preparation helps prevent mount flexing when using larger sway bars, ensuring proper handling and longevity.
Assembling Frame and Link Connections
With the mounting brackets securely installed and aligned, you can begin assembling the frame and link connections.
First, drill 3/8″ holes in the frame rails at marked positions, ensuring perpendicular alignment for maximum strength. Remove any rivet remnants on cross members before bolting. Using durable materials for mounting hardware can enhance the longevity of the assembly.
Slide lubricated D-bushings onto the stabilizer bar, then place U-plates over them, loosely bolting to the frame brackets with 3/8″ hardware. It is important to check for any excessive play in the sway bar link to prevent future suspension issues.
Next, position the end links vertically on the control arms with vehicle weight on. Mark hole locations, and drill 3/8″ holes.
Bolt the end link brackets to the control arms, keeping adjustable links loose if applicable. Leave all bolts initially loose to allow bar centering before final torque, ensuring smooth assembly movement and proper fitment.
Ensuring Proper Alignment
First, you’ll want to center those stabilizer bars just right. This step is key because it helps ensure that the weight is balanced, which in turn boosts your bow’s performance. Using a portable tongue weight scale can help verify that the load distribution remains optimal during tuning.
Once you’ve got that down, the next thing to do is adjust the link rotation. This part is super important because it keeps everything aligned properly. If things are off, you could end up with unwanted torque or misalignment, and nobody wants that!
Taking the time to do these steps carefully is really crucial. It makes a huge difference in achieving consistent aiming stability and executing your shots reliably. Achieving a neutral balance before introducing bias is foundational for effective tuning and shot consistency.
Centering Bars Accurately
Although achieving perfect balance requires multiple steps, centering your stabilizer bars accurately forms the foundation of proper alignment. Using the right hydrophobic properties in your equipment can also reduce unwanted movement caused by environmental factors.
Begin by observing the bubble level at full draw with eyes closed, then open to assess bow lean. If the bubble shifts left, move your center of gravity left by adjusting weight on the left back bar; if right, shift right accordingly.
Position back bars close to the bowstring with a slight downward angle to minimize vertical bias. This downward angle adjustment shortens the working length of the bar, making aim adjustments more responsive.
Use V-bar bracket click marks for precise, incremental adjustments, following the bubble’s direction. Adjust side rods and back bar distances to fine-tune lateral balance, verifying changes by shooting multiple arrows through target rounds.
Adjusting Link Rotation
After centering your stabilizer bars accurately, focus on adjusting the link rotation to ensure proper alignment. Begin by positioning the rod ends at a centered neutral point to prevent binding.
Adjust one end link first, then set the opposite to neutral height to avoid unnecessary re-adjustments of the drop link length general adjustment. Regular maintenance and correct alignment help maintain tire durability by reducing stress on trailer components.
Rotate the turnbuckle until the drop link lower M10 bolt aligns freely with the sway bar hole. Verify that the rod ends mount on the sway bar’s outside, with pinch clamps facing inward. Once adjusted, the turnbuckle mustn’t rotate against the rod ends when tightened.
Remember to:
- Align rod ends neutrally to avoid binding
- Face pinch clamps inward for clearance
- Confirm drop link bolt fits loosely in sway bar hole
- Mount rod ends outside the sway bar
- Lock turnbuckle rotation after adjustment
This guarantees ideal link function and prevents preload issues.
Final Torque and Safety Checks
When completing the installation of stabilizer bars, final torque application and safety checks guarantee long-term reliability and performance.
Use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten upper sway bar link nuts to 45 ft-lbs and lower nuts to 70 ft-lbs, or follow your vehicle’s factory manual for specific values.
Apply thread locker before torquing to prevent fastener loosening from vibrations.
Confirm fastener alignment visually to avoid cross-threading.
The B nut where the bar connects with the end link is especially critical to torque correctly to avoid clunking noises.
After installation, conduct multiple torque verifications, especially following a test drive, to ensure retention.
Listen for clunking noises within 30 minutes or 100 miles, indicating potential under-torquing.
Inspect endlink integrity and suspension geometry regularly during initial operation.
Document torque values and procedures for future reference.
Proper final torque and thorough safety checks prevent premature component failure and ensure safe, excellent stabilizer bar function.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Stabilizer Bars Be Installed on Any Vehicle Model?
You can’t install stabilizer bars on every vehicle model because fitment depends on specific make, model, and suspension geometry. Each vehicle has unique mounting points and end link angles, so you need bars designed for your exact platform.
Universal kits exist but only fit certain sizes and suspension types. Always check manufacturer compatibility lists and verify hardware matches your vehicle’s specs to guarantee proper installation and effective performance.
How Often Should Stabilizer Bar Bushings Be Replaced?
Like a worn-out shoe sole, stabilizer bar bushings should be replaced when you notice signs like squeaking or looseness.
Typically, rubber bushings last several years but degrade faster under harsh conditions. You should inspect them during routine services and replace them every 3-5 years or sooner if you drive rough roads.
Polyurethane bushings last longer and need less maintenance, often lasting beyond five years before replacement is necessary.
Will Adding Stabilizer Bars Affect Ride Comfort?
Adding stabilizer bars will slightly affect your ride comfort, especially on rough or uneven roads.
You’ll notice reduced body roll and improved handling, but stiffer bars may cause a harsher ride by transmitting more bumps through the suspension.
To balance comfort and performance, pair your sway bars with appropriate spring rates.
Keep in mind, front bars impact comfort less than rear ones, so adjust stiffness carefully to maintain ideal ride quality.
Are Professional Installation Services Recommended for Beginners?
You shouldn’t attempt stabilizer bar installation yourself if you’re a beginner.
Think of it like assembling a clockwork mechanism: every component must align perfectly under tension.
Professionals have the right tools and expertise to confirm precise torque and secure fittings.
This prevents safety risks and premature wear.
They save you time, reduce costly errors, and guarantee warranty coverage.
Can Stabilizer Bars Improve Towing Stability on Uneven Terrain?
Yes, stabilizer bars can greatly improve your towing stability on uneven terrain. They reduce lateral sway by limiting independent wheel movement, helping maintain consistent tire contact and traction.
This minimizes trailer fishtailing and enhances steering control during sudden maneuvers or crosswinds. However, guarantee proper installation and balanced loading, as excessive stiffness or improper setup can reduce effectiveness and increase suspension stress.
Use stabilizer bars alongside other towing safety measures for best results.
Every Bolt Counts: Your Last Line of Defense
Now that you’ve secured the mounting brackets and aligned the frame and link connections, don’t rush the final steps. Precision here isn’t just recommended—it’s critical. Tighten every bolt to the specified torque and double-check each connection for safety.
Skipping this could compromise your vehicle’s stability when it matters most. Remember, a properly hooked-up stabilizer bar isn’t just an upgrade; it’s your assurance of control and safety on every turn.